Dr. Sachin Mittal is the Best Gallbladder Stones Surgeon in Faridabad
Severe pain in the right upper
abdomen which may radiate to back.
• Nausea or vomiting
• Abdominal bloating (gas
formation)
• Intolerance to fatty foods
• Indigestion
Many patients don’t have
symptoms but they can become
symptomatic and cause complications
Timely management is necessary.
WHAT IS GALLBLADDER?
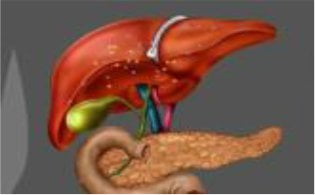
Gallbladder is a small pouch
present close to the
liver.
Its function is to
store and concentrate bile juice
which is produced in the
liver.
Bile is a juice
produced by the liver which
helps to digest fat.
WHAT ARE GALLSTONES (CHOLELITHIASIS)?
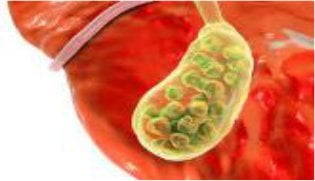
Stones forming within the
gallbladder.
They may vary
in number and size.
For
management size, shape or number
is not relevant.
WHO IS AT RISK FOR GALLSTONES?
• Women more than men.
•
People in their 30’s and
40’s.
• Overweight
men and women.
• People
with rapid/sudden weight
loss.
• Pregnant women.
Women on prolonged hormone
therapy.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
• Severe pain in the right upper
abdomen which may radiate to
back.
• Nausea or
vomiting.
• Abdominal
bloating (gas formation).
•
Intolerance to fatty foods.
•
Indigestion.
Many patients
don’t have symptoms but they can
become symptomatic and cause
complications.
Timely
management is necessary.
HOW ARE THE GALLSTONES DIAGNOSED?
• Abdominal Ultrasound.
•
Endoscopic Ultrasound.
•
Cholescintigraphy (HIDA
Scan).
• Endoscopic
Retrograde Cholangio
Pancreatography (ERCP).
•
Magnetic Resonance Cholangio
Pancreatography (MRCP).
WHAT IS CHOLECYSTITIS?
Cholecystitis is defined as
inflammation of the gall
bladder.
Commonly arise when
the flow of bile is interrupted
either due to stone (90%) or
infection of biliary tract.
• Severe abdominal pain.
•
Fever and Malaise.
• Nausea
and Vomiting.
Diabetic patient may have minimal
pain due to
neuropathy.
Complications:
Pancreatitis,
Gangrene, Empyema, Gall bladder
perforation.
WHAT IS GALL BLADDER POLYP AND ADENOMYOMATOSIS?
Cholesterolosis is deposition of
cholesterol crystals in the
gallbladder
wall.
Adenomyomatosis is
excessive proliferation of the
inner lining of gall bladder;
some has risk of gallbladder
malignancy.
Gall bladder
polyp includes projections of
the gallbladder wall into the
lumen.
Cholesterolosis and
adenomyomatosis are usually
silent.
Polyp >10 mm in
size or multiple need removal of
gall bladder.
BILIARY PANCREATITIS
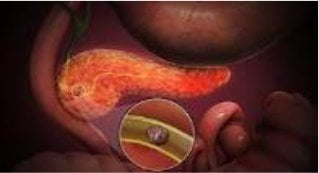
Defined as swelling of
pancreas.
Biliary
pancreatitis is a very serious
and life threatening
condition.
CAUSE
Gallbladder
stones migrate into the common
bile duct (CBD) and block the
pancreatic opening.
WHAT COMPLICATIONS GALL STONES CAN CAUSE?
• Pus formation in the
gallbladder (Empyema).
•
Jaundice and Cholangitis (life
threatening infection of biliary
system).
• Gangrene or
perforation of the
gallbladder.
• Acute
pancreatitis which can have a
catastrophic sequel of MODS and
other serious
complications.
• Cancer of
gallbladder if left untreated.
GALLBLADDER STONES AND ASSOCIATION WITH GALLBLADDER CANCER
Gall bladder with stones, if left
untreated for longer period has
higher chances of cancer.
•
More than 85% gallbladder
cancers have associated gall
bladder stones.
• Female
gender, multiple child births
and obesity are some factors
associated with higher risk of
developing gall bladder
cancer.
• Larger the
gallstones (more than 2-3 cm in
diameter), the greater the
association with gallbladder
cancer.
TREATMENT
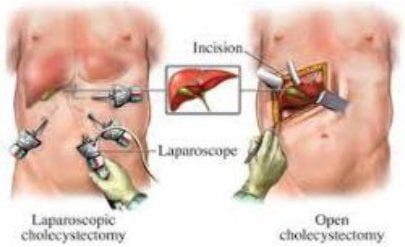
• Surgery to remove the
gallbladder (cholecystectomy) is
the only way to cure
gallstones.
• Conventional
(open) method, Laparoscopic
Cholecystectomy (Gold standard),
Scar less surgery
(Single
incision
laparoscopic surgery) SILS and
Robotic assisted Cholecystectomy
are the options.
• In
Laparoscopic or Robotic,
recovery usually occurs within a
day in the hospital.
WHAT IS LAPAROSCOPIC CHOLECYSTECTOMY?
• Surgeon makes few tiny holes in the abdomen and with help of special surgical instruments and a miniature telescope with mounted video camera, while watching the monitor the surgeon performs the surgery. Post-surgery holes are closed and no stitch is applied over it.
WHAT IS SCARLESS CHOLECYSTECTOMY (SILS)?
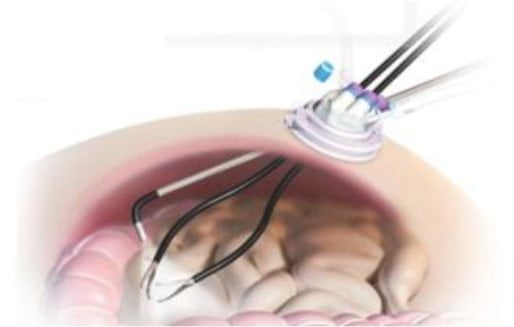
• Surgeon makes a small cut into the umbilicus and performs the entire surgery from that hole using special instruments.
WHAT IS ROBOTIC ASSISTED CHOLECYSTECTOMY?

robotic surgery photo
• Robotic surgery is of advantage
of minimal blood loss, more
precise dissection
and
minimal trauma.
BENEFITS OF ROBOTIC SURGERY
• 7 degrees of freedom.
•
Stable operative field.
•
3-D vision.
• Self camera
control.
• No hand
tremors.
• Better ergonomic
for surgeon.
WHAT IF A STONE SLIPS INTO THE COMMON BILE DUCT (CBD)?
• Slippage of the stone(s) in CBD
may cause pain or jaundice or
both.
• This situation
requires an endoscopy (ERCP) for
removing the stone(s).
•
This should preferably be done
before gall bladder surgery.
HOW DO WE CONFIRM A STONE IN THE CBD?
• Abdominal Ultrasound.
•
Endoscopic Ultrasound.
•
Cholescintigraphy (HIDA
Scan).
• Endoscopic
Retrograde Cholangio
Pancreatography(ERCP).
•
Magnetic Resonance Cholangio
Pancreatography(MRCP).
DO YOU ONLY REMOVE ONLY THE STONES FROM THE GALL BLADDER?
• No, the gall bladder is removed
with the stones.
• As the
disease is in the wall of the
gall bladder.
• Gall bladder
with stone is a non-functional
gall bladder.
WHAT IS ERCP Endoscopic retrograde cholangio pancreatography?
• Endoscope is inserted into the
stomach through mouth.
• Once
the endoscope is in the first
part of the small intestine, it
locates the affected bile duct.
An instrument on the endoscope
is used to capture the stone in
a tiny basket and removed with
the endoscope.
• Biliary
stent may be needed and placed
in the Common Bile Duct (CBD).
This may be
removed
endoscopically after
few weeks.
DO PEOPLE NEED GALLBLADDER?
• Yes, for storing bile but only
when it is functioning
normally.
• Gall bladder also
concentrates the bile. When
diseased, it starts over
concentrating the bile and
forming the stones.
•
Diseased gall bladder may be
contracted or thick wall may not
distend to store bile.
•
Gallbladder is an organ that
people can live without.
•
Once the gallbladder is removed,
bile production remains
unaffected as it is produced in
the liver.
• Gallbladder has
no role to play in that.
HOW LONG WILL I HAVE TO STAY IN THE HOSPITAL AFTER SURGERY?
The patient is discharged on the same day or next day of operation unless there is some associated medical problem.
INSTITUTE OF MINIMAL ACCESS, BARIATRIC AND ROBOTIC SURGERY
Institute of Minimal Access, Bariatric & Robotic Surgery, endeavours to provide the best healthcare, holistic recovery and rehabilitation services. The division comprises of surgeons who are leaders in their respective fields and are dedicated to performing surgical procedures through minimally invasive techniques (Key- Hole Surgery) including robotic techniques, so that patients reap the benefits of faster recovery, lesser post-operative pain and excellence cosmetic results.
